Ailments and Procedures >> Spine (Back)
- Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Discectomy
- Facet Injections
- Radio Frequency Lesioning
- Spinal Cord Stimulation
- Epidural Injections
- Sacroiliac Joint Lesioning
- Sympathetic Nerve Block
- Intrathecal Pain Pumps
- Disc Nucleoplasty
- Discography
Lumbar Discoscopic Discectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery technique that uses an endoscope to relieve pain caused by herniated discs pressing on nerve roots. An endoscope is a thin, long, and flexible viewing instrument with its own special lighting that allows me to see into the spinal discs.
The disc endoscope is inserted through a ¼ inch incision that will act as a ‘keyhole‘ for the entire procedure. The maneuverability of the endoscope allows the muscle and tissue to be dilated rather than being cut. This leads to less tissue trauma, less post-operative pain, quicker recovery times, earlier rehabilitation and an avoidance of general anesthesia.

The visualization gained by using the endoscope allows for elimination of the cause of the pain by removing only the portion of the disc’s core that is pressing on the nerve roots.
The procedure is performed in an outpatient setting. No hospitalization is needed. The surgery lasts for approximately 30 minutes and usually results in the patient resuming light activities on the evening of the surgery.
The facet joints, found on both sides of the back of the spine, can become painfully irritated or inflamed. A facet joint injection may help diagnose the source of a patient’s pain. It can also relieve pain and inflammation.
Radiofrequency (RF) Lesioning is a procedure using electrical impulses to interrupt nerve conduction on a semi-permanent basis. The nerves are usually blocked for 6 to 12 months. The procedure disrupts nerve conduction (especially conduction of pain signals) and it may reduce other related symptoms (numbness, tingling, or burning). Approximately 70-80% of patients will get good block of the intended nerve. This should relieve the pain that the blocked nerve controls. Once a nerve is blocked, it sometimes becomes clear that there is also some pain generated from different areas.

Since nerves cannot be seen on x-ray, the needles are positioned using bony landmarks that indicate where the nerves usually are. Fluoroscopy (x-ray) is used to identify those bony landmarks. A local anesthetic (like Novocain) is injected to numb superficial tissue. The special RF needle is then inserted under X-ray guidance. For most patients, the insertion of the RF needle will cause a dull pressure, not pain. After confirmation of the needle tip position, a special needle tip is inserted. When the needle is in good position, as confirmed by x-ray, electrical stimulation is done before the RF Lesioning. This stimulation may produce a buzzing or tingling sensation or may be like hitting your “funny bone”. You may also feel your muscles jump. You need to be awake during this part of the procedure so you can report to the doctor what you feel. The tissues surrounding the needle tip are then heated when electronic current is passed using the Radio Frequency machine, for 90-120 seconds. This “numbs” the nerves semi-permanently.
Spinal cord stimulation (also called SCS) uses electrical impulses to relieve chronic pain of the back, arms and legs. It is believed that electrical pulses prevent pain signals from being received by the brain. SCS candidates include people who suffer from neuropathic pain and for whom conservative treatments have failed.

The epidural steroid injection is the placement of cortisone, a powerful anti-inflammatory agent, into the epidural space, which approximates the disc and spinal column. The epidural injection has been used for over 40 years as treated for back pain. It involves using either steroids or anesthetic agents allowing good benefits with minimal risk factors. The main goal of the epidural injection is to shrink the swelling in bulging or herniated discs, and to decrease any inflammation that surrounds the disc and may be pressing on a spinal nerve.
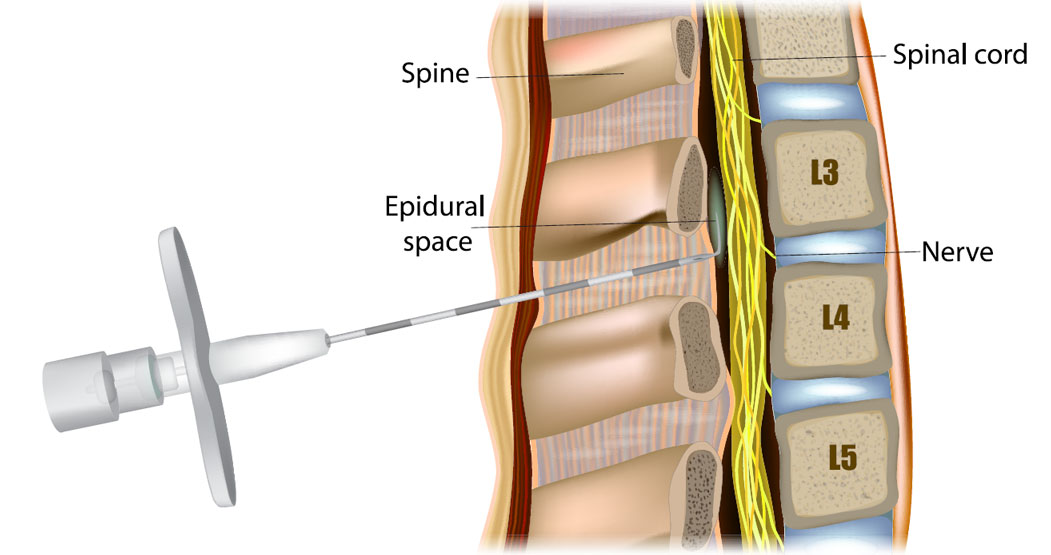
This is a common procedure. Because of the low risk and low incidence of any significant problems or side effects, it is felt to be a reasonable procedure to follow when traditional conservative therapy for disc pain has failed to provide improvement. A large percentage of patients upon whom this procedure is performed will get complete resolution of symptoms; a small percentage may experience no real improvement at all. It is generally an accepted practice that this procedure be repeated up to three times within a few months, although in some cases, additional injections may be administered. Injections may be given as a single dose, or once a week for up to three weeks. Additional injections have additive effects.
Side effects and adverse reactions are rare. Some of these potential (uncommon) side effects include fluid retention, “puffiness”, and rarely acne. An additional risk is the possibility for the epidural needle to nick the dura (the covering of the spinal cord). Should this occur, there could be leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, which could cause a severe “spinal headache”. If this should happen, bed rest and an increase in fluid and caffeine intake frequently will alleviate the headache completely. Should this not resolve the problem, it could be necessary to do what is called a “blood patch” in which (under sterile conditions) blood is removed from a vein in the arm and placed in the same epidural space. This completely resolves symptoms of the headache. The incidence of a spinal headache is approximately 1 in 1,000, and occurs in a patient about once every year. As you can see it is very rare. Since this is the most common adverse event that may occur from epidural injections, the remaining potential complications should not worry you, but make you more informed. Other potential risks include: worsening of symptoms, bleeding infections, backache, steroid side effects, bowel or bladder dysfunction, hematoma, cord compression, paralysis, neurological damage or impairment, or death. One of the most serious side effects (which is extremely rare) is the developing of an epidural infection or abscess. In order to avoid these complications, the procedure is done under strict sterile conditions, utilizing fluoroscopy to localize the epidural space and guide the needle.
If there is improvement from the steroid epidural, it likely will occur over the next several days to two weeks. The improvement should not be expected immediately.
Patients are advised to rest on the day of the epidural, although bed rest, while preferable, is not required. By the next day, previous activities can be resumed. An occasional patient will feel such significant relief that they are tempted to resume various strenuous activities. They are cautioned not to do this, however. It is generally advised to pursue a course of gradual increase in activity. Often coordinated with physical therapy or other training once the injections have been completed. Patients are usually seen 3-7 days following the procedure for a follow-up exam, to evaluate their response to the steroid epidural(s).
A sacroiliac joint injection is an injection of an anesthetic with a long lasting steroid (“cortisone”) in the Sacroiliac joint(s). The sacroiliac joints are located in the back where the lumbosacral spine joins the pelvis. They are paired (right and left) and are surrounded by a joint capsule like the finger joints. The steroid injected reduces the inflammation in the joint space. This can reduce pain, and other symptoms caused by inflammation.
The procedure is performed with the patient lying on their stomach with fluoroscopic (x-ray) guidance. The patients are monitored with EKG, blood pressure cuff and blood oxygen-monitored device. The skin in the back is cleaned with antiseptic solution and then the injection is carried out. After the injection, you are placed on your back or on your side. The immediate effect is usually from the local anesthetic injected. This wears off in a few hours. The cortisone starts working in about 5 to 7 days and its effect can last for several days to many months.
Sympathetic Nerves are a network of nerves that extend the length of the spine and control some of the crucial involuntary functions of the body such as the opening and narrowing of blood vessels. Sympathetic Nerve Blocks work directly on this network of nerves.
With a standard nerve block, a local anesthetic is injected around a nerve, preventing pain messages traveling along that nerve pathway from reaching the brain. Standard never blocks are typically used to relieve pain for a short period of time, such as during a surgery. A Sympathetic Nerve Block is performed to determine if there is damage to the sympathetic nerve chain and whether it is the source of pain. This is a diagnostic test primarily, but it may provide relief far in excess of the duration of the anesthetic.
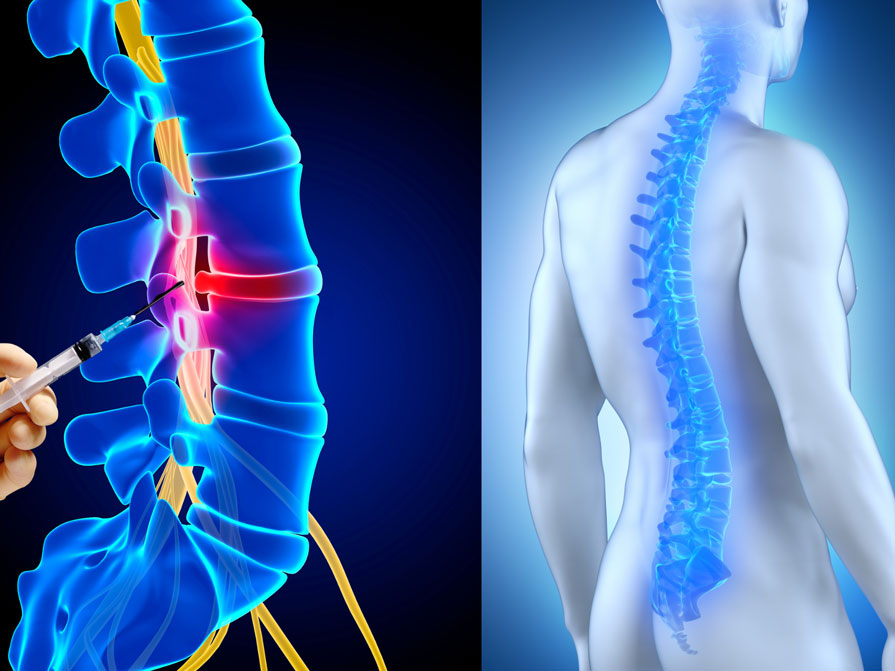
The procedure starts with a local skin anesthetic given in the lumbar area of the back. A needle is then inserted into the back under fluoroscopic vision next to the vertebral body. An anesthetic medication is then injected into the area. If necessary, the block may be performed on both sides of the spine.
It takes thirty minutes for the procedure followed by evaluation and recovery for several hours.
The system consists of a pump and catheter, both of which are surgically placed under the skin. The pump is implanted in the abdominal area, just above or below the beltline. A thin, flexible tube, called a catheter, connects to the pump and is tunneled under the skin to the site where medication is to be delivered. The pump releases the medication at the set rate, and the medication flows from the pump, through the catheter, to the site of delivery in the intrathecal space.
Intrathecal drug delivery works directly on the spinal cord, which is the highway for pain signals. This therapy is thought to work by interfering with pain signals before they reach the brain. They can offer good to excellent pain relief, and improve your ability to go about daily activities.
On average, the procedure takes about 1 to 2 hours from start to finish. Typically, the implant is performed under comfortable sedation.

Nucleoplasty is a minimally invasive treatment for contained herniated discs. In nucleoplasty, advanced radio-frequency devices are used to remove soft tissue in open and minimally invasive spinal surgery. Tissue is ablated and coagulated through molecular disintegration, with only minimal thermal damage to surrounding tissue.
In some cases, nucleoplasty is the answer to quick, lasting relief — but without the drugs or major surgery associated with other methods.
Although it is surgery, the procedure is relatively simple — more like getting a vaccination or steroid injection. It’s minimally invasive.

Directed to the precise source of the pain, the radio waves work to gently dissolve small amounts of unwanted spinal disc tissue, thus reducing the pressure in the disk. It’s the pressure that can cause lower back and upper leg pain.
Nucleoplasty disc decompression is considered a “conservative” approach to pain management, much on the order of pain drugs, epidural steroid injections and physical therapy, he said, as opposed to radical approaches requiring more invasive surgical techniques.
To understand what a contained herniated disc looks like, one should think of a bicycle tire with a bulge in it. When a bulge or “herniation” appears in the shell of a disc, severe pain can result. This is because the disc is surrounded by sensitive nerve roots.
When the bulge becomes large enough to come in contact with these nerve roots, the sensation of pain can radiate throughout the lower back and upper legs.
So, in much the same way that a bulging tire can be reduced by releasing some of the air, a herniated disc can be treated by relieving pressure inside the disc.
The procedure begins with a local anesthetic and light sedative. With the patient awake, small amounts of raidio wave energy are released into the damaged disc through a catheter-like device that is about the thickness of a dime.
The energy creates a reaction at the molecular level that dissolves some of the spongy tissue inside the damaged disc. Then, as pressure inside the disc is reduced, the herniation in the shell retracts. Irritation to the nearby nerve roots is eliminated, and pain is relieved.
Typically, the entire nucleoplasty radio wave injection procedure takes 20 to 30 minutes, and the patient is ready to walk out of the clinic in about an hour.
According to clinical studies, the results are about the same as those of traditional disc surgeries — but with a big difference. “With nucleoplasty, the patient does not experience the trauma, lengthy recovery period, high cost, or most other potential complications,” the doctor said.
Based on these studies, he said, approximately four out of five nucleoplasty patients have seen successful results as measured by patient satisfaction scores, reduced pain, absence of narcotics use, and return to work.
This diagnostic procedure, also called discogram, is used to determine whether back pain is caused by one or more spinal discs. The procedure involves pressurizing suspect discs with an injection of sterile liquid to induce pain. Discography helps the specialist plan a course of treatment.


